Beyond 24fps: The financial facets of High Frame Rate filmmaking
As the boundaries of cinematic innovation expand, the advent of High Frame Rate (HFR) filmmaking heralds a new era. However, it also adds new layers of complexity to the financial aspects of film production.

This comprehensive guide explores the costs of High Frame Rate filmmaking, helping producers and directors to navigate this exciting yet challenging terrain.
What is High Frame Rate filmmaking?
HFR filmmaking refers to the process of shooting scenes at a frame rate significantly higher than the standard 24 frames per second (fps) conventionally used in cinema. With frame rates like 48fps or 60fps, HFR filmmaking creates smoother motion and enhances visual clarity, transforming the cinematic experience.
The advantages and disadvantages of High Frame Rate filmmaking
Advantages of High Frame Rate
HFR filmmaking delivers enhanced visual clarity and realism, producing smoother and more fluid motion. This immersion can create a profound cinematic experience. Think of Peter Jackson's "The Hobbit" trilogy, shot at 48fps, which aimed to engross viewers in the fantastical world of Middle Earth.
Disadvantages of High Frame Rate
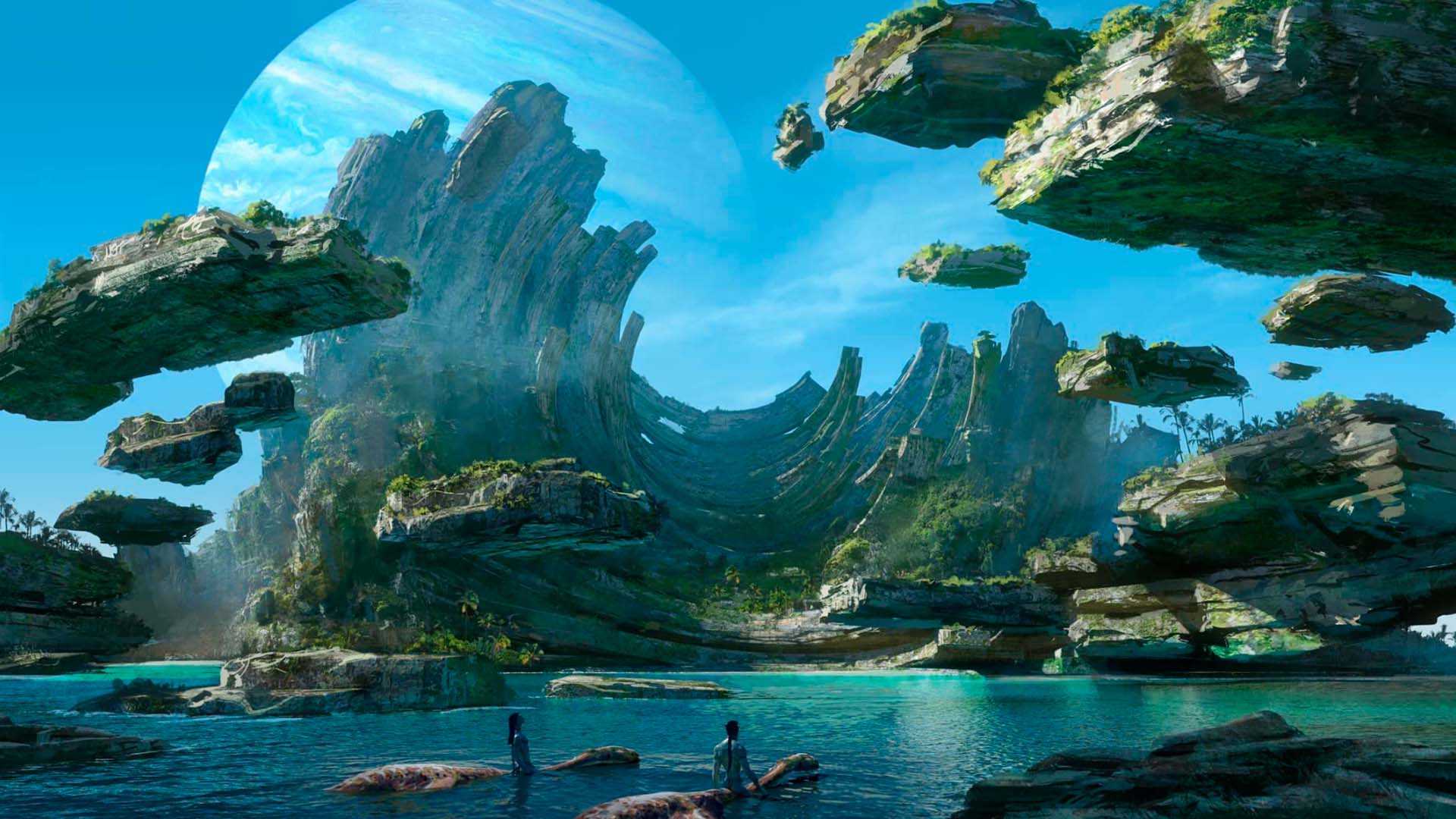
Despite these advantages, HFR filmmaking faces certain drawbacks. The production costs are significantly higher due to more demanding equipment, post-production requirements, and talent considerations. Furthermore, HFR's hyper-realistic visuals can inadvertently impact artistic aesthetics, diverging from traditional cinematic 'look and feel.' James Cameron's "Avatar 2" (2022), delayed partly due to HFR-related technical challenges, stands as a testament to these constraints.

Understanding the cost factors in High Frame Rate filmmaking
The financial implications of HFR filmmaking stem from several cost factors:
- Equipment and camera technology: HFR requires advanced cameras capable of capturing high frame rates, leading to increased expenses.
- Post-production requirements: The editing and grading processes for HFR footage can be more complex and time-consuming.
- Talent and crew considerations: Working with HFR may require specialized skills from both talent and crew, affecting overall production costs.
- Visual effects and CGI: Creating visual effects in HFR is an intricate process that can significantly inflate the budget.
Case Studies: Examples of High Frame Rate films and their costs
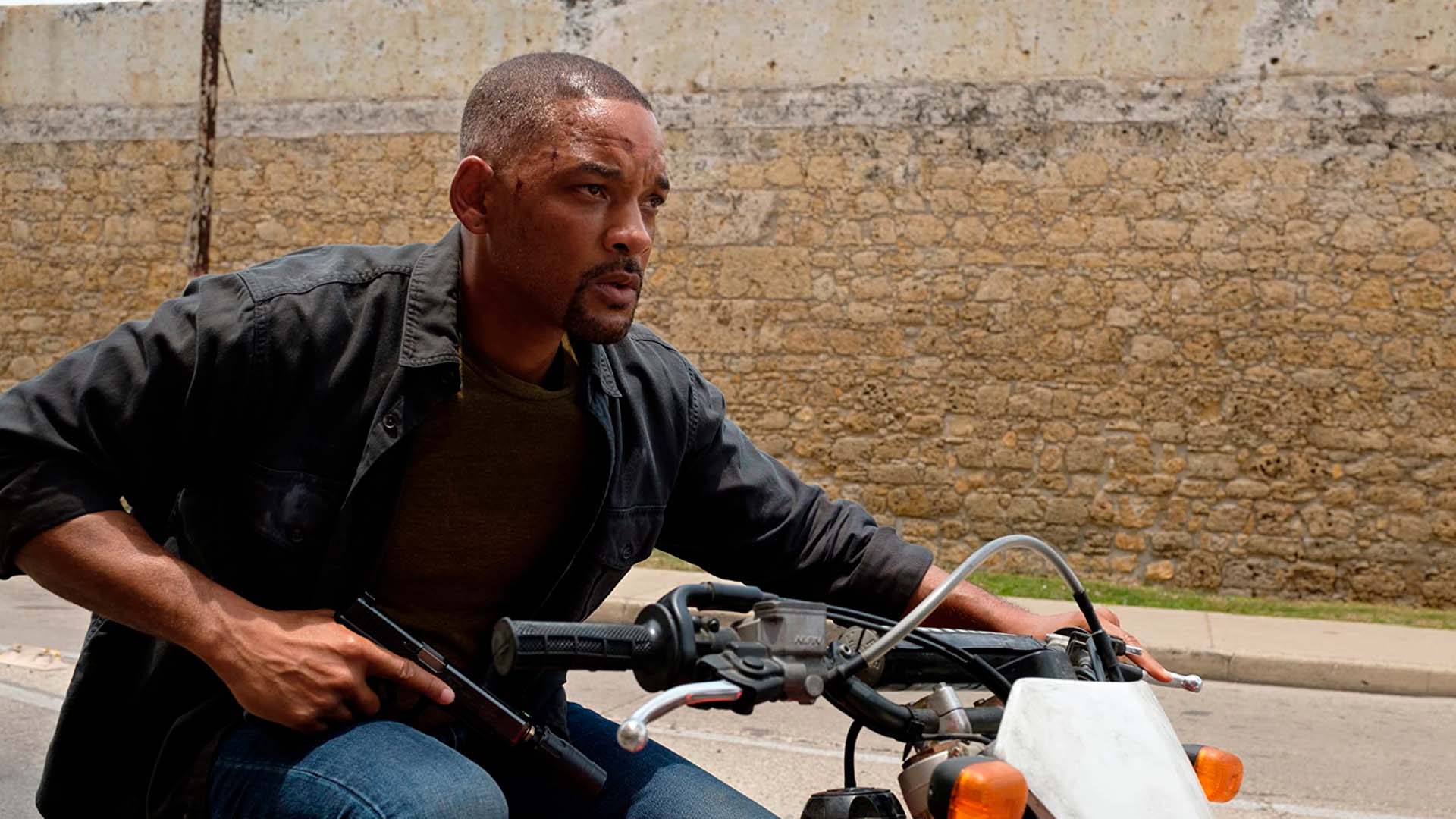
"Gemini Man" (2019) by Ang Lee was a full-blown HFR project, shot in 3D at 120fps. While the film's visual spectacle was impressive, the production costs skyrocketed to an estimated $138 million.

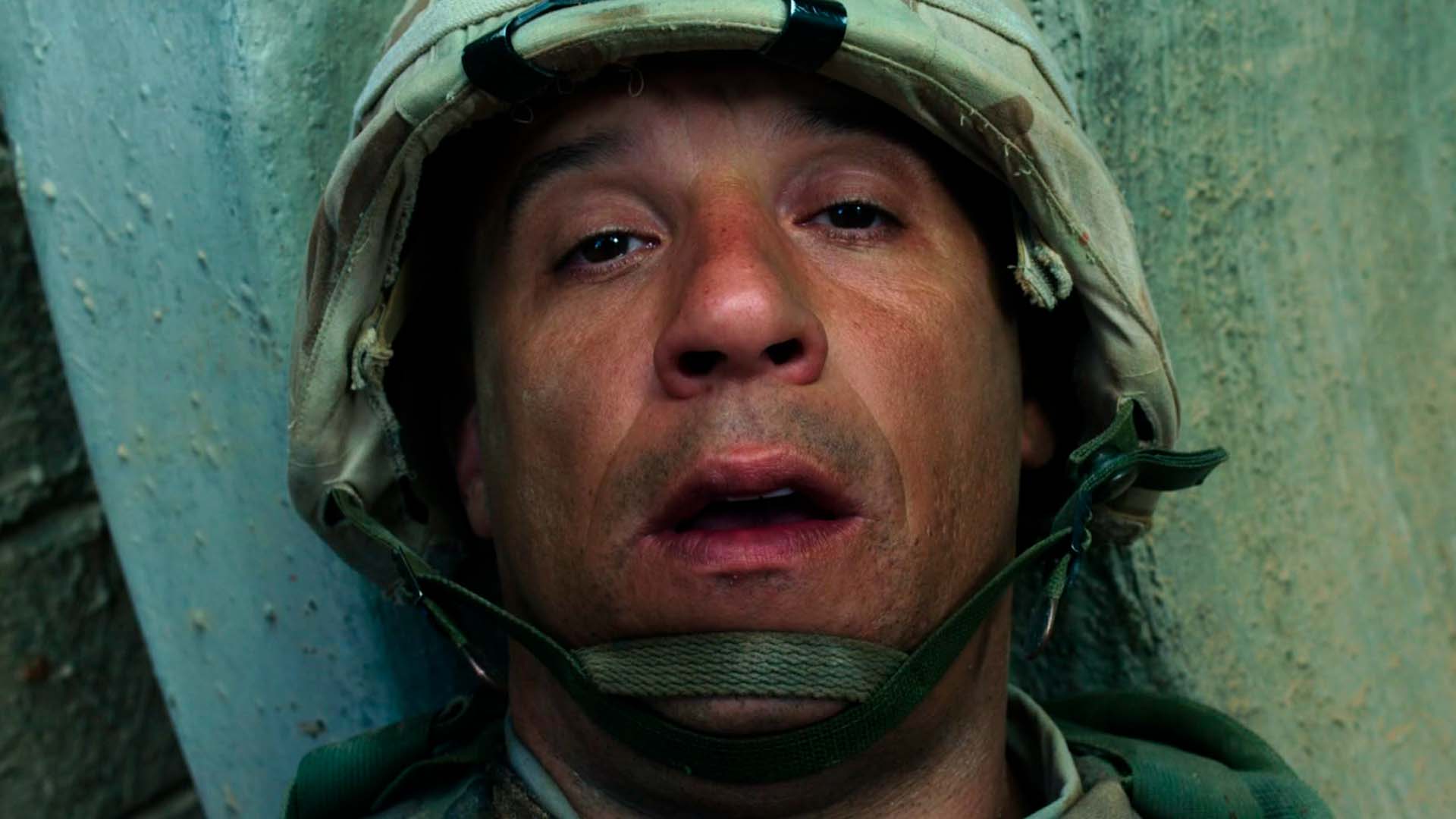
Similarly, "Billy Lynn's Long Halftime Walk" (2016) pushed HFR to its limits, but its box-office earnings didn't match the high production costs, signaling caution for future HFR ventures.

Strategies for budgeting and cost management in High Frame Rate filmmaking
Navigating the costs of High Frame Rate filmmaking requires strategic budgeting and cost management:
- Prioritize key scenes: Consider shooting only vital sequences in HFR to balance costs while maintaining visual impact.
- Leverage technology: Utilize tech advances to mitigate the costs associated with HFR, such as cloud-based post-production solutions.
- Detailed pre-production planning: Thorough budgeting during pre-production can help avoid unexpected costs later on.
Conclusion
HFR filmmaking offers a new frontier in cinematic experience but understanding the financial impact of High Frame Rate filmmaking is crucial. Exploring cost factors, analyzing case studies, and implementing effective budgeting strategies can pave the way for more cost-effective HFR productions.
Filmustage, an innovative filmmaking platform, supports filmmakers in this journey, providing solutions that streamline production workflows, foster collaboration, and aid in the realization of creative visions, whether they are shot in traditional 24fps or venture into the realm of High Frame Rate filmmaking.
From Breakdown to Budget in Clicks
Save time, cut costs, and let Filmustage’s AI handle the heavy lifting — all in a single day.